AI/ML Enhancement Project - Describing labelled EO Data with STAC
Introduction
The use of the SpatioTemporal Asset Catalogs (STAC) format is crucial when it comes to describing spatio-temporal datasets, including labelled Earth Observation (EO) data. This allows to describe the labelled EO data while defining standardised sets of metadata to delineate its key properties, such as spatial and temporal extents, resolution, and other pertinent characteristics. The use of STAC brings several benefits, including enhancing the reproducibility and transparency of the process and its result, as well as ensuring that the data becomes discoverable and accessible to other stakeholders (e.g. users, researchers, policymakers, etc).
This post presents User Scenario 3 of the AI/ML Enhancement Project, titled “Alice describes the labelled EO data”. It demonstrates how the enhancements being deployed in the Geohazards Exploitation Platform (GEP) and Urban Thematic Exploitation Platform (U-TEP) will support users describing labelled EO data using the STAC format.
To demonstrate these new capabilities defined in this User Scenario, an interactive Jupyter Notebook is used to guide an ML practitioner, such as Alice, in the process of exploiting the STAC format to describe, publish, and search labelled EO data, including:
- Loading a labelled EO data (
.geojsonfile) and display it asgeopandasdataframe - Show labelled EO data on an interactive map
- Generate a STAC Item and add metadata to it
- Publish the STAC Item on dedicated S3 and on the STAC endpoint
- Search the STAC Item using using STAC API and query parameters
Practical examples and commands are displayed to demonstrate how these new capabilities can be used from a Jupyter Notebook.
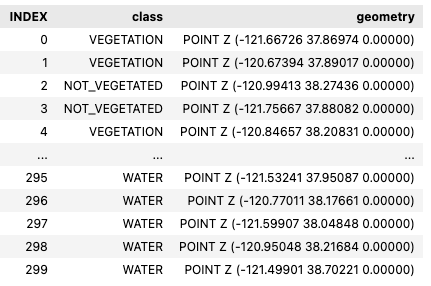
Loading labelled EO data
A .geojson file of the labelled EO data was loaded into the notebook and converted into a geopandas dataframe.
import geopandas as gpd
import geojson
fname = './input/label-S2A_10SFH_20230519_0_L2A.geojson'
with open(fname) as f:
gj = geojson.load(f)
# Make geodataframe out of the created object
gdf = gpd.read_file(fname)
gdf
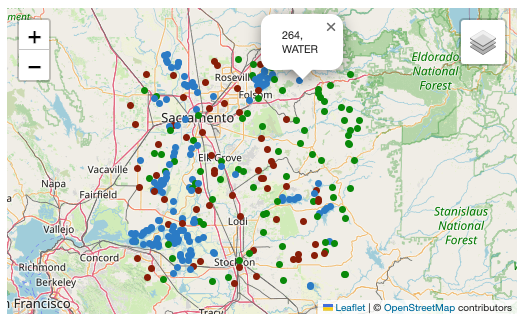
The Python library folium was then used to display the labelled EO data on an interactive map.
import folium
from folium import GeoJson, LayerControl
# Get extent and center of dataframe points
bbox = (gdf.geometry.total_bounds)
centerx,centery = (np.average(bbox[1::2]), np.average(bbox[::2]))
# Create map
map = folium.Map(location=[centerx, centery], tiles="OpenStreetMap", zoom_start=9)
# Add Labels to map
map = addPoints2Map(gdf, map)
# Add layer control
LayerControl().add_to(map)
# Visualis map
map
Generate STAC Item
Before creating the STAC Item, the user defines the geometry of the vector data represented by the dataframe.
# Get geometry of dataframe points
label_geom = geojson.Polygon([[
(bbox[0], bbox[1]),
(bbox[2], bbox[1]),
(bbox[2], bbox[3]),
(bbox[0], bbox[3]),
(bbox[0], bbox[1])
]])
The user can now create the STAC Item and populate it with relevant information, by exploiting the pystac library.
import pystac
# Creating STAC Item
label_item = pystac.Item(
id="<label_id>",
geometry=label_geom,
bbox=list(bbox),
datetime=datetime.utcnow(),
properties={},
)
The user defines a dictionary named label_classes to represent the classes for a classification task. The dictionary contains the class names for various land cover types, such as vegetation, water, clouds, shadows, and more. This mapping can be used to label and categorise data in a classification process.
The user can then apply the label-specific STAC Extension with the defined label classes.
from pystac.extensions.label import LabelExtension, LabelType, LabelClasses
# Define label classes
label_classes = {
"name": "CLASSIFICATION",
"classes": [
"NO_DATA",
"SATURATED_OR_DEFECTIVE",
"CAST_SHADOWS",
"CLOUD_SHADOWS",
"VEGETATION",
"NOT_VEGETATED",
"WATER",
"UNCLASSIFIED",
"CLOUD_MEDIUM_PROBABILITY",
"CLOUD_HIGH_PROBABILITY",
"THIN_CIRRUS",
"SNOW or ICE",
],
}
# Apply label-specific STAC Extension “LabelExtension” with its related fields
label = LabelExtension.ext(label_item, add_if_missing=True)
label.apply(
label_description="Land cover labels",
label_type=LabelType.VECTOR,
label_tasks=["segmentation", "regression"],
label_classes=[LabelClasses(label_classes)],
label_methods=["manual"],
label_properties=["CLASSIFICATION"],
)
# Add geojson labels
label.add_geojson_labels(f"label-{label_id}.geojson")
# Add version
version = ItemVersionExtension(label_item)
version.apply(version="0.1", deprecated=False)
label_item.stac_extensions.extend(
["https://stac-extensions.github.io/version/v1.2.0/schema.json"]
)
In the end, the user validates the created STAC Item.
# Validate STAC Item
label_item.validate()
display(label_item)
Publish the STAC Item
The STAC endpoint and STAC Collection in which to publish the STAC Item are firstly defined:
stac_endpoint = "https://ai-extensions-stac.terradue.com"
collection = read_file("input/collection/collection.json")
Subsequently, the STAC Item can be posted on a dedicated S3 bucket.
# Define filename and write locally
out_fname = f"item-label-{label_id}.json"
pystac.write_file(label_item, dest_href=out_fname)
# Define wrapper to write on S3 bucket
wrapper = StarsCopyWrapper()
exit_code, stdout, stderr = (
wrapper.recursivity()
.output(f"s3://ai-ext-bucket-dev/svv-dataset/{label_id}")
.config_file("/etc/Stars/appsettings.json")
.extract_archive(extract=False)
.absolute_assets()
.run(f"file://{os.getcwd()}/{out_fname}")
)
When the STAC Item is posted on S3, it can be published on the dedicated STAC endpoint.
# Define customized StacIO class
StacIO.set_default(CustomStacIO)
# Read catalog.json file posted on S3
catalog_url = f"s3://ai-ext-bucket-dev/svv-dataset/{label_id}/catalog.json"
catalog = read_url(catalog_url)
ingest_items(
app_host=stac_endpoint,
items=list(catalog.get_all_items()),
collection=collection,
headers=get_headers(),
)
Find STAC Item on STAC Catalog
Once the STAC Item is successfully published on the STAC endpoint, it can be searched using pystac and pystac_client libraries. These libraries enable users to interact with a STAC catalog by defining specific query parameters, such as time range, area of interest, and data collection preferences. Subsequently, only the STAC Item(s) that align with the provided criteria is(are) retrieved for the user.
# Import libraries
import pystac
from pystac_client import Client
# Access to STAC Catalog
cat = Client.open(stac_endpoint, headers=get_headers(), ignore_conformance=True)
# Define query parameters
start_date = datetime.strptime(“20230601”, '%Y%m%d')
end_date = datetime.strptime(“20230630”, '%Y%m%d')
bbox = [-121.857043 37.853934 -120.608968 38.840424]
tile = “10SFH”
# Query by AOI, start and end date
query_sel = cat.search(
collections=[“ai-extensions-svv-dataset-labels”],
datetime=(start_date, end_date),
bbox=bbox,
)
item = [item for item in query_sel.item_collection() if tile in item.id][0]
# Display Item
display(item)
Conclusion
This work demonstrates the new functionalities brought by the AI/ML Enhancement Project to help a ML practitioner exploiting the STAC format to describe, publish, and search labelled EO data, including:
- Loading a labelled EO data (
.geojsonfile) and display it asgeopandasdataframe - Show labelled EO data on an interactive map
- Generate a STAC Item and add metadata to it
- Publish the STAC Item on dedicated S3 and on the STAC endpoint
- Search the STAC Item using using STAC API and query parameters with
pystac
Useful links:
- The link to the Notebook for User Scenario 3 is: https://github.com/ai-extensions/notebooks/blob/main/scenario-3/s3-describingEOdata.ipynb
Note: access to this Notebook must be granted - please send an email to support@terradue.com with subject “Request Access to s3-describeEOdata” and body “Please provide access to Notebook for AI Extensions User Scenario 3” - The user manual of the AI/ML Enhancement Project Platform is available at AI-Extensions Application Hub - User Manual
- Link to the project update article “AI/ML Enhancement Project - Progress Update”
- Link to User Scenario 1 article “AI/ML Enhancement Project - Exploratory Data Analysis”
- Link to User Scenario 2 article “AI/ML Enhancement Project - Labelling EO Data”